AES encryption using BCrypt library and C++ on Windows
In this post I’m going to briefly talk about the BCrypt library on Windows. More specifically using the library for encryption using the AES algorithm.
The Windows API is very well documented here. In summary, the encryption can be done in the following steps:
- Obtain a handle to the cryptographic algorithm provider.
- Generate a symmetric key using the cryptographic algorithm provider.
- Obtain the size of the cipher text for the block by providing the plain text, the symmetric key, and and an initialization vector.
- Allocate memory for the cipher text and perform the encryption by providing the plain text, the symmetric key, and the initialization vector.
- Similarly decryption can be performed by providing the cipher text, the symmetric key and the same IV used to encrypt the block (each block is ideally encrypted using a different IV).
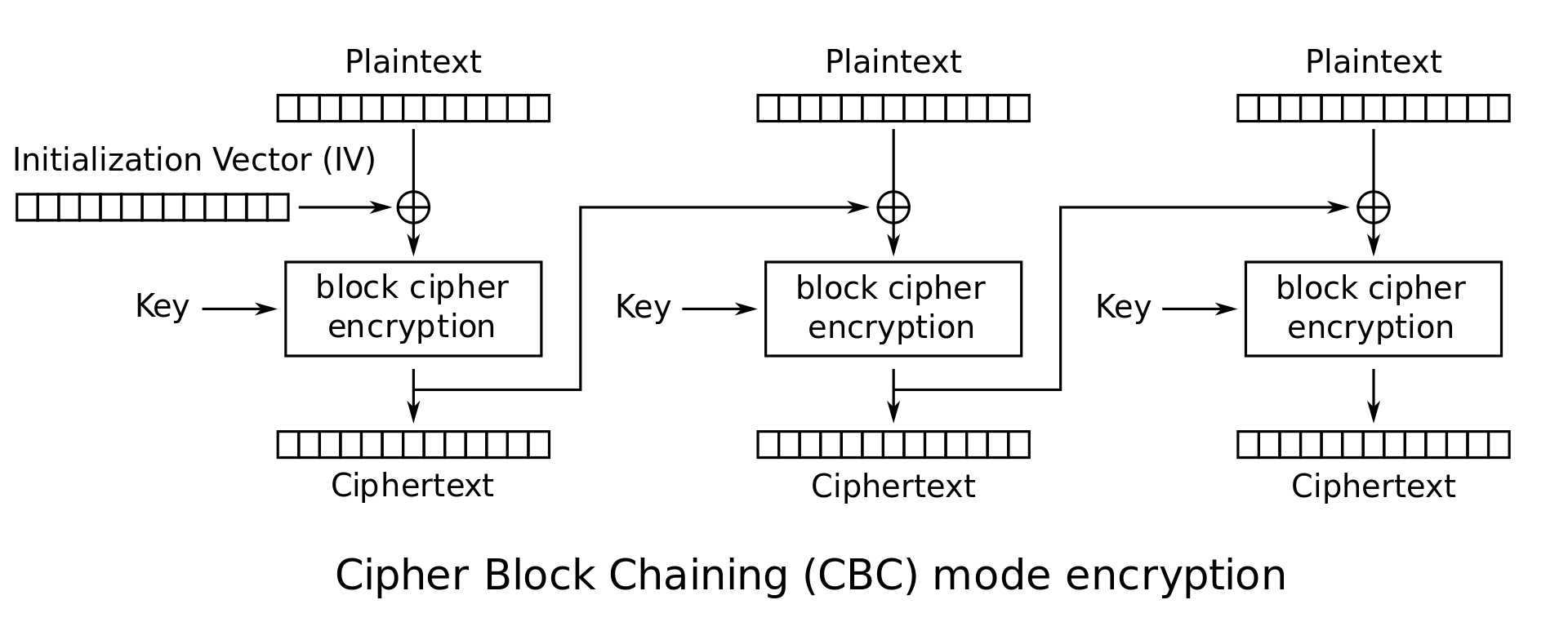 source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Block_cipher_mode_of_operation#Cipher_block_chaining_(CBC)
source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Block_cipher_mode_of_operation#Cipher_block_chaining_(CBC)
Let’s write some code:
// main.cpp
#pragma comment( lib, "bcrypt" )
// C API headers
#include <Windows.h> // bcrypt.h has a dependency on this header
#include <bcrypt.h> // crypto API
// C++ API headers
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <exception> // std::exception
#include <vector>
#include "Utils.h"
const BYTE AES256KEYSIZE = 32;
const WCHAR messageToEncrypt[] = L"It is a sunny day today 🌞 but tomorrow it is going to rain 🌧!";
const WCHAR initializationVector[] = L"my initialization vector"; // TODO: Replace with your IV
int main()
{
BCRYPT_ALG_HANDLE hBcryptAlg = nullptr;
BCRYPT_KEY_HANDLE hBcryptKey = nullptr;
BYTE rgAESKey[AES256KEYSIZE] = {}; // TODO: Replace with a random key
int retVal = 0;
try
{
ErrorHandler(BCryptOpenAlgorithmProvider(&hBcryptAlg, BCRYPT_AES_ALGORITHM, nullptr, 0));
ErrorHandler(BCryptGenerateSymmetricKey(hBcryptAlg, &hBcryptKey, nullptr, 0, rgAESKey, AES256KEYSIZE, 0));
std::vector<UCHAR> vPlainText(sizeof(messageToEncrypt));
memcpy(vPlainText.data(), messageToEncrypt, vPlainText.size());
std::cout << "Plain text:\n";
HexDump(vPlainText);
std::vector<UCHAR> vInitializationVector(sizeof(initializationVector));
memcpy(vInitializationVector.data(), initializationVector, vInitializationVector.size());
// calculate the size of the cipher text
ULONG cbCipherText = 0;
ErrorHandler(
BCryptEncrypt(
hBcryptKey,
vPlainText.data(),
vPlainText.size(),
nullptr,
vInitializationVector.data(),
vInitializationVector.size(),
nullptr,
0,
&cbCipherText,
BCRYPT_BLOCK_PADDING));
// now allocate ciphertext buffer and encrypt!
// note that initialization vector is modified after each call to BCryptEncrypt
// ideally data should be encrypted in chunks while re-using the updated IV for the subsequent chunk
std::vector<UCHAR> vCipherText(cbCipherText);
ErrorHandler(
BCryptEncrypt(
hBcryptKey,
vPlainText.data(),
vPlainText.size(),
nullptr,
vInitializationVector.data(),
vInitializationVector.size(),
vCipherText.data(),
vCipherText.size(),
&cbCipherText,
BCRYPT_BLOCK_PADDING));
std::cout << "After encryption:\n";
HexDump(vCipherText);
// clear the plaintext
memset(vPlainText.data(), 0, vPlainText.size());
ULONG cbPlainText = 0;
// reset the initialization vector to the initial value
memcpy(vInitializationVector.data(), initializationVector, vInitializationVector.size());
ErrorHandler(
BCryptDecrypt(
hBcryptKey,
vCipherText.data(),
vCipherText.size(),
nullptr,
vInitializationVector.data(),
vInitializationVector.size(),
vPlainText.data(),
vPlainText.size(),
&cbPlainText,
BCRYPT_BLOCK_PADDING));
std::cout << "After decryption:\n";
HexDump(vPlainText);
}
catch (const std::exception& e)
{
std::cout << e.what() << std::endl;
retVal = -1;
goto CLEANUP;
}
CLEANUP:
if (hBcryptAlg)
{
BCryptCloseAlgorithmProvider(hBcryptAlg, 0);
}
if (hBcryptKey)
{
BCryptDestroyKey(hBcryptKey);
}
return retVal;
}
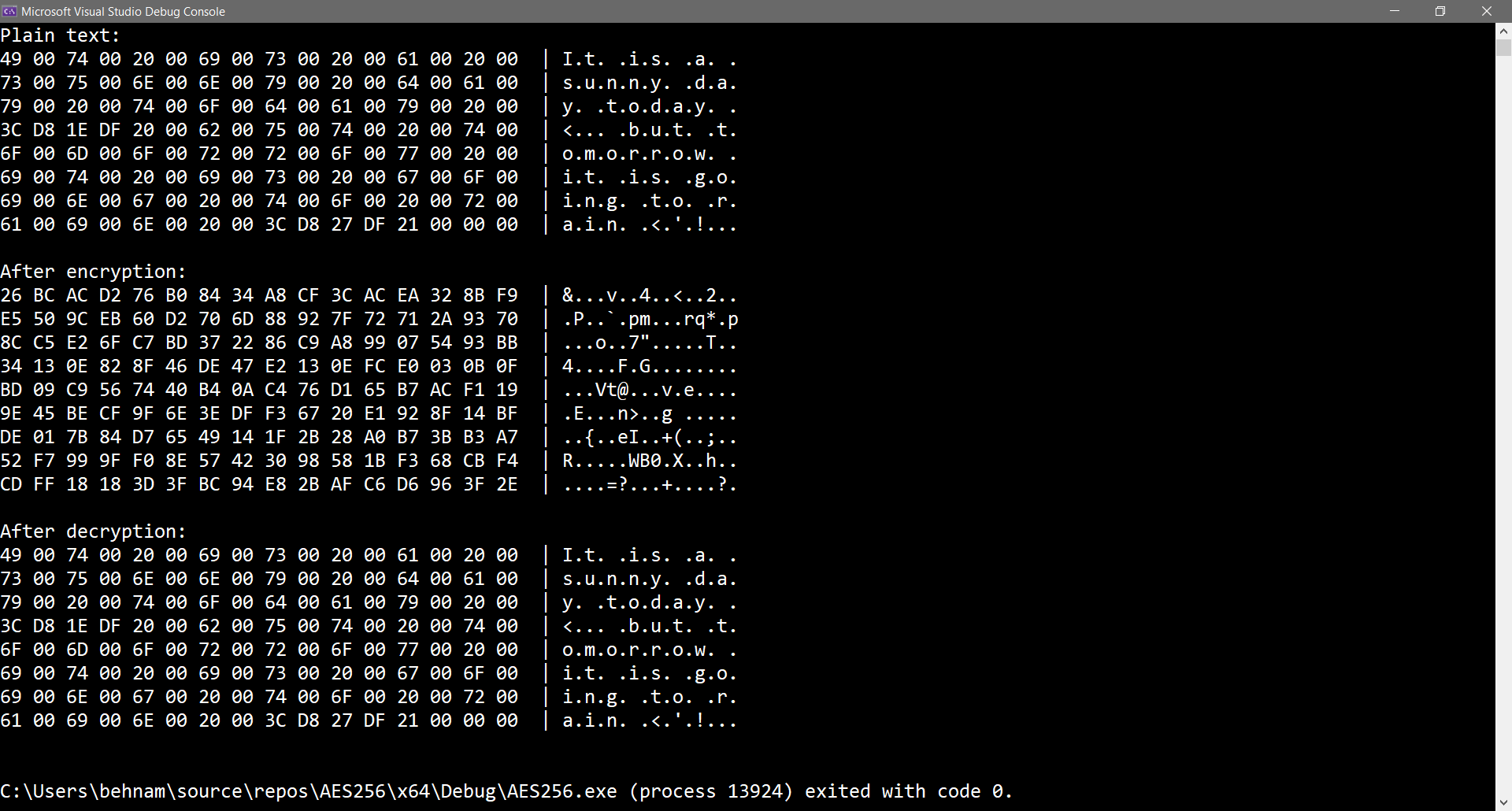
The output of the program looks like the following:
The above C++ code uses the utility functions from the following header/source files:
// Utils.h
#pragma once
void ErrorHandler(NTSTATUS status);
void HexDump(const std::vector<UCHAR> & vByteBuffer);
// Utils.cpp
#include <Windows.h>
#include <ctype.h> // isprint
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <vector>
#include <exception> // std::exception
// macros from ntstatus.h
#define STATUS_NOT_FOUND ((NTSTATUS)0xC0000225L)
#define STATUS_BUFFER_TOO_SMALL ((NTSTATUS)0xC0000023L)
#define STATUS_SUCCESS ((NTSTATUS)0x00000000L)
void ErrorHandler(NTSTATUS status)
{
switch (status)
{
case STATUS_NOT_FOUND:
throw std::exception("No provider was found for the specified algorithm ID. ");
break;
case STATUS_NO_MEMORY:
throw std::exception("A memory allocation failure occurred.");
break;
case STATUS_INVALID_PARAMETER:
throw std::exception("One or more parameters are not valid.");
break;
case STATUS_BUFFER_TOO_SMALL:
throw std::exception("The size of the key object specified by the cbKeyObject parameter is not large enough to hold the key object.");
case STATUS_INVALID_HANDLE:
throw std::exception("The algorithm handle in the hAlgorithm parameter is not valid.");
case STATUS_SUCCESS: // success
// no-op
break;
default:
throw std::exception("Unknown failure.");
break;
}
}
void PrintHexChunk(const std::vector<UCHAR>& vByteBuffer, size_t upToIndex)
{
std::cout << " | ";
for (size_t j = upToIndex - 16; j < upToIndex; ++j)
{
if (isprint(vByteBuffer[j]))
{
std::cout << vByteBuffer[j];
}
else
{
std::cout << ".";
}
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
void HexDump(const std::vector<UCHAR>& vByteBuffer)
{
static const CHAR hexChars[] = "0123456789ABCDEF";
std::string textChars;
textChars.resize(16);
size_t j = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < vByteBuffer.size(); ++i)
{
if (i != 0 && i % 16 == 0)
{
PrintHexChunk(vByteBuffer, i);
j = i;
}
std::cout << hexChars[(vByteBuffer[i] >> 0x04)] <<
hexChars[(vByteBuffer[i] & 0x0F)] << " ";
}
// print the remaining bytes
std::cout << " | ";
while (j < vByteBuffer.size())
{
if (isprint(vByteBuffer[j]))
{
std::cout << vByteBuffer[j];
}
else
{
std::cout << ".";
}
++j;
}
std::cout << std::endl << std::endl;
}